- Home
- Center for the Advancement of Teaching & Learning
- Teaching & Learning Resources
- Artificial Intelligence and Your Teaching
Artificial Intelligence and Your Teaching
Artificial Intelligence and Your Teaching
ChatGPT and other generative artificial intelligence (AI) tools are making headlines within and beyond higher education and continues to be an ever evolving and complex topic. AI in learning can produce high quality products – from text, images, to sound clips – creating an interesting tension between rich partnerships and concerns over academic integrity, with particular emphasis on the future of assessment. Like many institutions, Elon has been exploring the impact of AI on and off our campus and has outlined suggestions for faculty. We’ve curated some helpful information for you to consider as you think about how AI might impact your teaching, course design, and student learning.
Opportunities to enhance and engage learning.
ChatGPT and other AI tools and platforms are… an opportunity to engage with our students in new educational paradigms that promote a more equal and creative relationship between the educator and the learner…
Rossi, V. (Feb 13, 2023). Perspectives on the use of ChatGPT for PGCert courses. Advancing Practice in Academic Development. [Blog]
Challenges to authentic, deep, and integrity-led learning are not new to higher education, in fact, everyday technologies such as the Google search have presented concerns around student learning. With students sharing that they are using AI more frequently in their learning than we may realize, it might feel as though you’re being forced to move to handwritten, oral, or in-class assessments. However, we encourage you to consider how you might partner with AI rather than outright ban it, and that AI can provide rich, meaningful, and creative assessments for learning.
As with any technology or instructional approach, integration of AI into student learning should be grounded in evidence of its effectiveness for learning within the context of your course, reflect alignment with learning outcomes and engagement approaches, and consider both authentic and transparent pedagogy and assessment. Creating assessments and activities appreciative of these factors, coupled with a scaffolded approach to assessment design, emphasizes the process of learning rather than the product, helping students lead with integrity, particularly within the context of AI use.
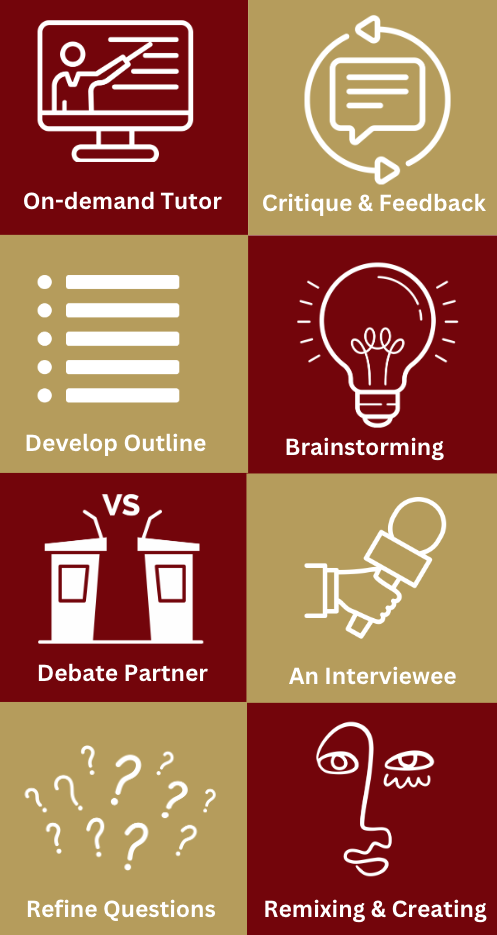
Below offers eight ways AI can support students partnering with AI during the learning process:
- One-on-one virtual tutoring on course subjects or pre-requisite/supplementary knowledge;
- Offering specific feedback on student work, or students critiquing and analyzing the work of AI;
- Creating initial outlines for assignments;
- Offer brainstorming of new ideas, insight into alternative ways of thinking, or help narrow a topic;
- Be a debating partner, helping students build and find flaws or gaps in arguments;
- Help students refine their discussion or research questions, exploring the importance of how you ask a question;
- Take the role of an interviewee, allowing students to chat with a specific historical, fictional, or contemporary person or perspective;
- Provide opportunities for students to create art or remixes across genres; and
- If you’re looking for helpful tips on creating writing assessments that partner with AI, check out Writing Across the University’s considerations for teaching writing with generative-AI.
If, on the other hand, you are looking for ways to discourage the use of AI in assessments, intentional assessment design can create opportunities where students are less likely to find value in misusing AI:
- Create learning activities and reflections of learning that related to ongoing class discussions or experiences or relies on students connecting learning to their own unique lived experiences.
- Have students submit multiple drafts of work, encouraging them to articulate how they’ve incorporated changes and why.
- Focus on the use of primary resources such as newspaper articles, interviews, diaries, or even the Elon archives.
- Integrate multiple modalities for demonstrating learning into an assignment such as concept or mind mapping, visual and textual collages, photo diaries, or podcasting, etc.
- Use class time for working on sections of an assignment.
Additional Resources
Looking for more examples of learning activities and assessments with the use of AI? Check out the resources below.
- Our friends at the Center for Writing Excellence have considerations for teaching writing with generative-AI and related faculty/staff Fall 2023 programming.
- Check out The Writing Center’s statement on bringing AI-enhanced writing to The Writing Center (updated August 2023).
- Colleagues across the internet have crowd sources a collection of 101 Creative ideas to use AI in education. A collection curated by #creativeHE. This ebook provides a variety of assessment examples from across disciplines that have integrated AI.
- Michael V. Drake Institute for Teaching and Learning at The Ohio State University offers examples of both learning goals and active learning approaches with AI on their Artificial Intelligence and Instruction page.
- The Center for Teaching Excellence at UVA offer a collection of curated articles on Generative AI in Teaching and Learning. Posts include “What is Generative AI”, “What Can I Do to Prepare to Teach with AI?” to “Leveraging AI in Assignments”.
Developing Transparent Course Policies
Integration of AI into student learning will look different for each student and each course. Good practice emphasizes being transparent and clear about the expectations around AI partnership in your course and for each assessment. Students may engage in academic dishonesty when the boundaries of partnership with AI are not clear. The continuum below provides a visualization of ways students may partner with AI in their learning, from the traditional fully learner-generated product to a completely AI created piece of work. To support students being successful in their learning and meeting the expectations of the Elon Honor Code, explicitly share with students what plagiarism and acceptable use (with and without attribution) looks like when engaging with AI in your course.

Below is language you may wish to use for your syllabus to help guide your articulation of expectations to students around AI use. As you decide how and when to allow or encourage AI use, consider your context (course and disciplinary), how you intend to use AI throughout the process of learning, and how you can engage students with intentional dialogue around integrity-led use of AI within and beyond your course.
When thinking about what you may wish to put in your syllabus, how to talk to students about AI use in your course, or how you might integrate AI into your course, consider the following questions:
- Do students (and I) know what AI is and how it works? Have you offered a definition for what AI-generated content is?
- What are ways that students might want to use AI in this course? What is the student’s responsibility for articulating their use of AI in their learning?
- What will happen if a student misuses AI in this course?
- Does the permitted use of AI vary between learning activities and assessments?
- Does the use of AI for learning activities and/or assessments help support students in meeting the intended learning goals?
- Do students know how I will (or won’t) be using AI in this course? How will I model appropriate, critical, and ethical use of AI for students?
- How do I define inappropriate use of AI in the context of this course? How is it defined in the context of my discipline?
- How is AI impacting my discipline/field of work? What are the skills associate with AI that students might need beyond this course?
Additional Resources
Below are additional resources to help you articulate to students the use of AI in their learning within the context of your course.
- What is my position on AI use is a helpful decision tree outline that you can use to determine how students can (or should) use generative AI tools in your course.
- The Sentient Syllabus Project (2023) by Boris Steipe offers example statements for a syllabus with specific language for various assessment types and the presence of AI.
- Lance Eaton has been collating classroom policies for AI generative tools from faculty globally.
Creating Course Materials (i.e., How can AI help you?)
AI has also emerged into our own work – Writing Across the University and Belk Library can support you exploring AI in writing and scholarship – and can also help in our teaching preparation. If you’re looking to try out tools like ChatGPT, we suggest some of the following examples:
- Design an outline for a syllabus,
- Brainstorm course topic structure/timeline,
- Draft learning outcomes,
- Develop a lesson plan,
- Create a rubric,
- Generate quiz/test questions,
- Provide examples of what student responses might be to an assignment or learning activity,
- Outline a slidedeck,
- Offer supplementary information for Moodle (i.e., summaries),
- Refine essay or discussion prompts.
It’s important to note that you should never be entering student work into an AI tool without permission, this is why providing feedback and grading are not on the list of suggested examples.
Additional Resources
Looking for more about how AI generated course materials? Check out the resources below.
- Faculty and teachers from around the world have been crowdsourcing prompts for developing course materials – such as learning outcomes, assessments, and learning activities. AI Prompts for Teaching offers a variety of tested prompts, allowing you to use them to draft materials for your own course or even to explore and practice using AI tools.
- The A Teacher’s Prompt Guide to ChatGPT aligned with ‘What Works Best’, offers example prompts for educators to use in AI tools to create assignments and activities focused on high expectations, explicit teaching, effective feedback, and assessment.
How can I talk to my students about this?
One of the best ways to approach AI and its impact on learning is to create space for student discussion and reflection on the topic. Beyond explicit course policies, talking to students about what AI is, how it can be used, their experiences with it, and the impact on learning can help students understand how to engage with AI in ways that support the Elon Honor Code.
Below are discussion prompts you may wish to use to hold a short discussion in your class:
- What do you know about artificial intelligence?
- How is generative AI similar to other tools you regularly use (i.e., Google search, Wikipedia, the calculator)? How is it different?
- Have you used any AI applications before? If so, how? Were they helpful? If you haven’t, why not?
- Is AI always right? Why or why not? How do you know if AI is being truthful?
- Do AI apps stop you from learning? How might AI help you learn?
- What are ways you can see yourself using AI in this classroom?
- What mistakes might you discover when integrating AI into your learning?
- What are examples of when using AI go against the Elon Honor Code? How does this break the Elon Honor Code?
AI systems and apps present a range of ethical and global concerns, from perpetuating bias, creating inequitable learning experiences, to having significant and profound impacts on our natural environment. Helping students understand how using of AI impacts the world around them can support them in being informed and critical users of these tools. Below are a few prompts and additional resources that you can use in your classroom:
- What are the ethical implications of the use of AI?
- What are the implications of AI in professional and practice settings? What are skills needed to ethically engage and utilize AI?
- Are certain voices or ideas elevated through AI?
- How and where is data entered into AI being stored? How do you know how that data is being used?
- How might you feel if your personal data or work were entered into a tool like ChatGPT? Does someone have the right to use your own work in generative AI tools?
Additional Resources
Looking for more about how to support students in thinking about the integration of AI into their work? Check out the resources below.
- Cardiff University and Sheffield Hallam University collaborated on two student-facing guides – Using Generative Artificial Intelligence – A Student Guide and Guidelines on Using AI in Academic Assessments.
Conclusion
These are a few helpful tips and resources to begin your journey with AI and your teaching. We encourage you to think about how building student competencies for being ethical and critical users of AI may be helpful for future employment or being professionals within your discipline. Reach out to CATL if you would like to discuss this topic in more depth, consider how you may develop assessments that utilize AI, or how you can approach discussing the topic in your class.